
Editor’s Note: This post was originally published in August of 2018 and has been updated for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
When looking for new products or goods online, 70% of people start with a search engine like Google.
Fewer and fewer people are heading directly to a brand website as their first stop than ever. Developing a solid ecommerce SEO strategy is critical to landing new customers and loyal buyers.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through the best practices of ecommerce SEO in 2021 to help you rank your products on SERPs and get your brand in front of the customers you want.
Let’s jump in!
What is ecommerce SEO?
Ecommerce SEO — is it any different than a traditional SEO strategy?
Yes and no.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the marketing practice in which you implement a set of best practices to increase your visibility on organic search results.
The goal of SEO is to generate more organic traffic and sales for your ecommerce business.
An ecommerce SEO campaign consists of doing the same thing (focusing on organic visits) with the following goals:
- Driving more traffic to your product pages and ecommerce store
- Building organic sales that you don’t have to spend ad money to get
- Creating better organic brand awareness on keywords/products
You might be thinking something like this: “My sales are fine, and many people find me organically already. Why do I need to put time and effort into ecommerce SEO?”
Well, it’s extremely important to focus on because ranking your product pages or store content on the first page of Google takes work. Lots of it.
If you rank on the second, third, or even fourth page of Google, you won’t generate much traffic (if any at all). Less than 1% of users ever reach the second page of Google.
Meaning you have to nail the best practices for many ecommerce SEO factors.
If you aren’t doing any SEO but are driving organic traffic, then you are likely shooting far below your potential.
Let’s discuss the best practices to guarantee more sales for your store.
Top three ecommerce SEO categories
Just like traditional SEO, ecommerce SEO can be split into three categories:
- On-page: On-page optimization refers to the improvement of your site’s code and content to improve rankings. It’s called “on-page” as the changes you make are visible to visitors.
- Off-page: Off-page SEO involves all the activities you perform outside of your site to improve results, such as link building.
- Technical: Technical SEO is the practice of optimizing your overall website’s performance to provide a better experience and, thus, increase your rankings.
Some people argue that technical SEO is part of on-page optimization.
In some ways, it is, but technical SEO is a huge practice that involves multiple optimizations, so it’s worth referring to it as a different category.
For the sake of brevity, we’ll focus on the long-hanging fruit of ecommerce SEO: On-page and technical optimization.
Let’s break them down.
MOST ECOMMERCE WEBSITES STRUGGLE WITH GENERATING CONSISTENT SALES…WE FIX THAT!
Since 2009, we have helped many ecommerce businesses dramatically increase their online sales. Let us do it for you!
What is on-page SEO in ecommerce?
Google can’t read a page like a human does.
When customers visit your ecommerce site, they can easily identify titles, descriptions, images, and videos.
Google doesn’t.
Instead, search engines look at your code and identify “clues” that tell them what your site is about.
If you look at your site’s code, you’ll see a bunch of “tags” that categorize the actual content of your site. These tags help search engines understand your site and match your pages to specific search queries.
For instance, any text between the tag “<title>” will help Google identify a title.
The tag “<a href>” indicates a hyperlink.
On-page SEO is the strategic optimization of this code to rank product pages, category pages, and even your entire ecommerce site for a primary keyword (or a set of keywords).
Let’s explore the most important best practices for on-page optimization.
Ecommerce title tags
Your title tag on a given product or category page on your website looks like this in organic search results:
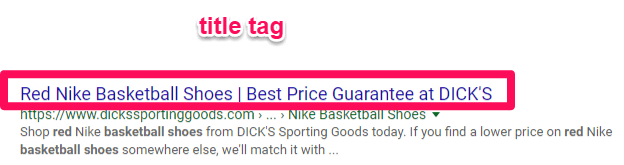
Title tags for ecommerce are the HTML codes that develop clickable titles/headlines for organic search results.
Title tags serve a few key functions when it comes to SEO impact. Title tags are great for providing relevance and increasing your organic click-through rate by appealing to customers searching for products.
For instance, the title tag above came up after a search for red basketball shoes.
The closer that your title tag relates to the keyword searched, the more likely users are to click.
One company was able to generate a 62% increase in organic traffic by updating their title tags for SEO.
Title tags are a critical piece of on-page SEO for ecommerce.
Depending on what ecommerce platform you use, you should be able to easily edit your title tag for products, category pages, and more.
For example, on Shopify, you can find this in the search listing preview for your products:

So, how do you optimize it?
Here are some best practices to keep in mind when crafting a title tag for your store:
- Place relevant keywords at the forefront title tags.
- Include LSI keywords if applicable/natural.
- Limit your length to 50-60 characters.
- Create unique titles for every single product page/category. Never duplicate.
- Consider utilizing your brand name at the end to develop better brand awareness.
Ecommerce meta description tags
Like your title tags, a meta description tag is an HTML code that helps explain the content of your page to users on a search engine. Unlike the title tag, you can’t click on the meta description text.
This appears on organic search results as a paragraph description just below the title tag:
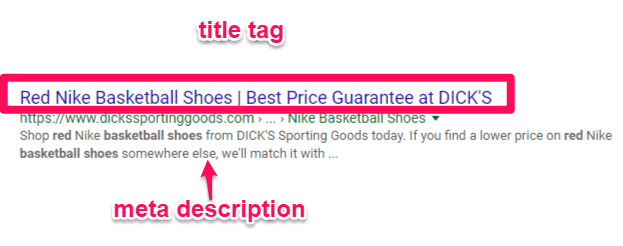
While inserting relevant keywords and context into your meta description is great, it doesn’t directly boost SEO.
So, why is it important? Because it creates the context for the user and helps dramatically increase CTR.
In fact, one brand found a 48% increase in organic clicks by improving their metadata.
Optimizing your meta description to improve CTR takes testing and great copywriting.
Here are some best practices to follow:
- Always include your primary keyword or keyword variations. They show up highlighted in bold to attract more attention.
- Focus on compelling descriptions that generate clicks.
- Avoid clickbait since it can increase your bounce rate. A high bounce rate is a bad signal that could harm your ranking potential.
Like your title tag, you should be able to edit your meta description where you edit on-page data. The exact location will depend on your platform.
For Example, here’s what the page looks like where you can edit your title tags and meta descriptions with BigCommerce:
Search engine friendly URLs
If you search for anything on Google, you’ll likely notice URL strings immediately:

Why? Because they display a company’s brand name. And since they’re highlighted in green, they draw your attention.
Do they actually make an impact for ecommerce sites? Absolutely.
A poor URL structure is confusing for searchers who are looking for your products and for search engines that are scanning your pages.
For example, when you analyze the following two SERP results, which product category page URL looks more appealing to click?
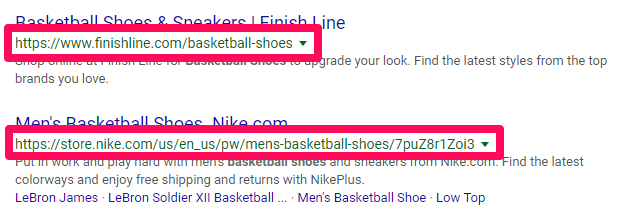
Are you drawn to the first one that’s simple and contains just the keyword, or do you like the long-string URL with dozens of random number combinations?
Probably the first one.
Absolute URLs like the first SERP page are what Google prefers.
When optimizing URL structure, platforms like Shopify and BigCommerce even pack tools to streamline the process:
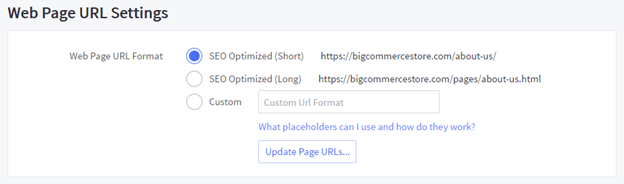
Here are some best practices to follow when creating your URL structure:
- Place your target keyword in the URL.
- Keep URLs as short and clean as possible.
- Stick with absolute URLs rather than dynamic or date-based URLs.
- Consistency is key. Stick with the same format on your entire store.
Category/product content
Content is king, right? Absolutely.
According to Orbit Media, the more content you produce in both B2B and B2C (ecommerce, too), the more results you get.
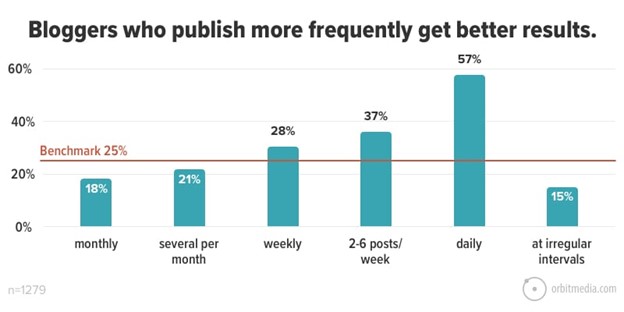
It’s no secret that producing great content can help you build everything from brand awareness to real sales for your products.
But when it comes to category pages or product pages, what do you do?
Do you write a long-form blog post? Not necessarily.
Category and product pages are tricky. You don’t want to have thin content and struggle to rank organically, but you don’t want to bombard buyers with tons of writing just for the sake of search engines.
This factor is potentially the most important aspect of optimization on your product pages.
Great product information not only educates the user and fulfills their number-one need, but it also gives search engines context on your page.
You can see one of the best examples of stellar ecommerce product page content from Bolthouse Farms:
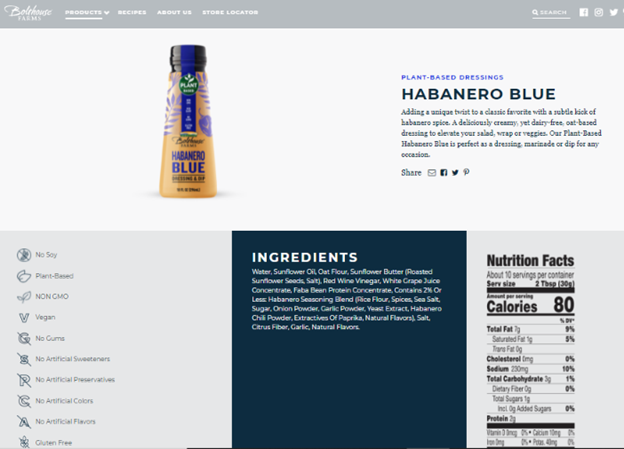
Keeping the product description short and sweet allows the potential buyer to understand what the product is without reading a full article.
LSI keywords are sprinkled in the description and among the side panel, too, which provides extra context on related searches.
Similarly, Surf Station has stellar category pages:
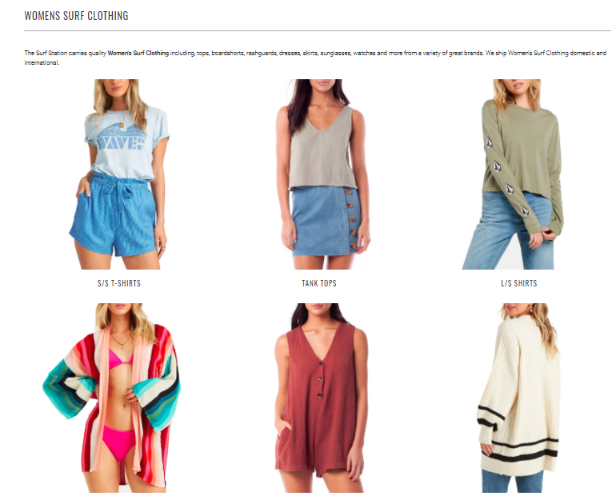
Each category page uses visuals to showcase the entire product offering within that category.
A rich description compels you to continue shopping with them.
And potential conversion roadblocks and pain points are demolished by a list of value propositions — all while containing LSI keywords to capture more topics.
When crafting your own product and category pages, here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Prioritize your top product and category pages first. Find your top pages in Google Analytics and make those a priority:
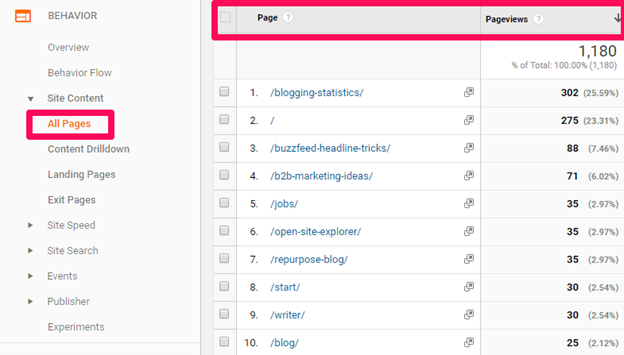
- Perform keyword research to find semantic words to sprinkle in your copy with a tool like LSIGraph. Just plug in your product or category to generate keyword ideas:
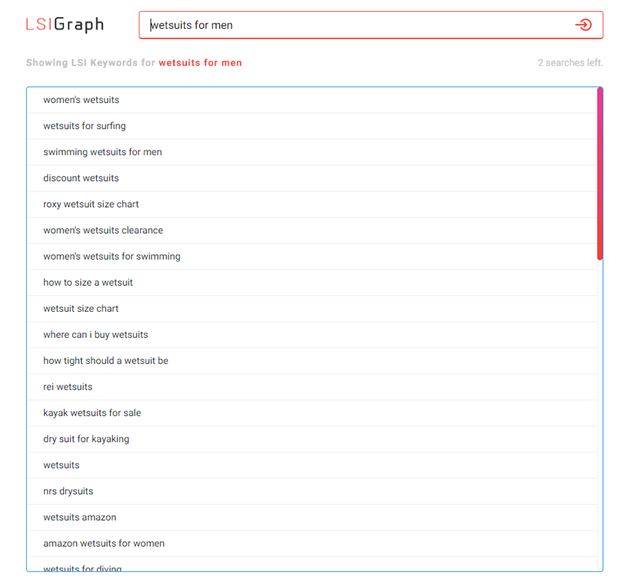
- Include your target head keyword as the title of the page.
- Optimize meta descriptions.
- Keep it short, sweet, and informative. Make it enjoyable to read.
Rich snippets
Ranking on Google is great, but if people don’t click on your pages, rankings won’t help your ecommerce business that much.
Here’s where rich snippets come in handy.
Rich snippets help search engines better understand your site’s content and display additional information on search results (e.g. star ratings for reviews). They might look like this:
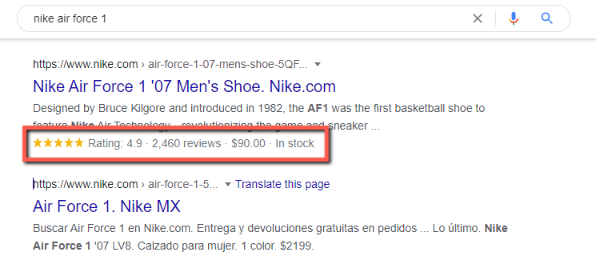
As you can see, rich snippets help you stand out in Google’s search results compared to those pages that don’t have them, which can increase your CTRs.
In terms of reviews, there are different types of snippets you can add, including author, item reviewed, ratings, and more.
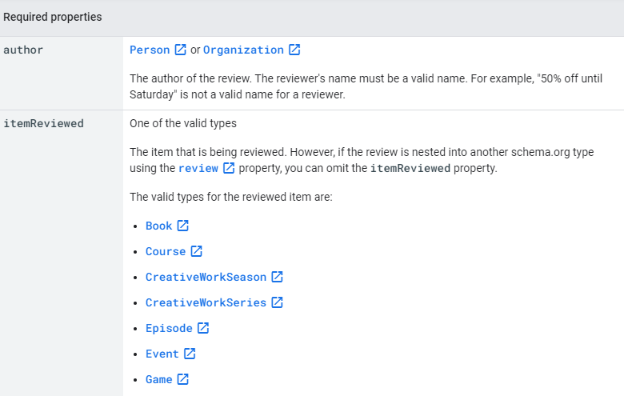
You can explore the complete list of review snippets here.
The question is: How can you add rich snippets to your ecommerce website?
You can do it manually, but you need a bit of coding knowledge.
Fortunately, Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper can help you implement rich snippets more easily.
Simply head over the tool, select “Products,” and type in the URL of a specific product page.
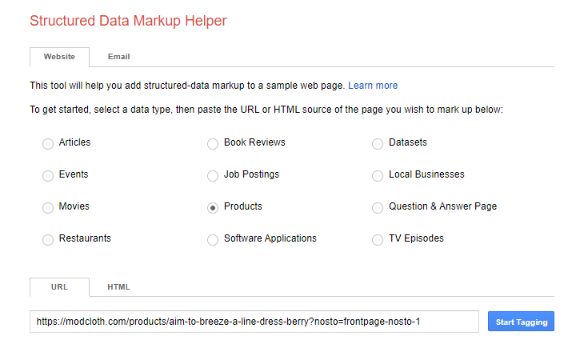
Then, click on “Start Tagging.”
Google will then show a “copy” of your site. You only need to highlight the data you want to display on search results.
For instance, if you want to display reviews, select the review section in your page and add relevant data (e.g. name of the reviewer, date of the review, etc.).
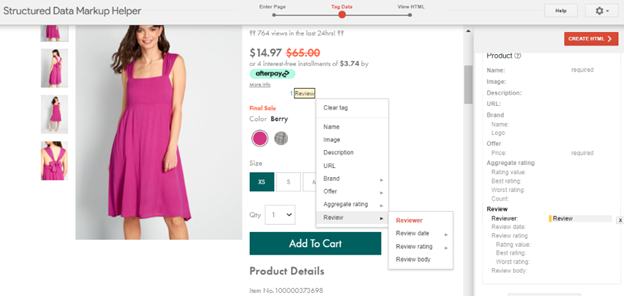
If you want to display star ratings, highlight the stars in your page and select “aggregate rating.”
You can play with the tool and explore the different elements you can select.
Once you’re done, simply click on “Create HTML.”
The tool will provide you with a piece of code.
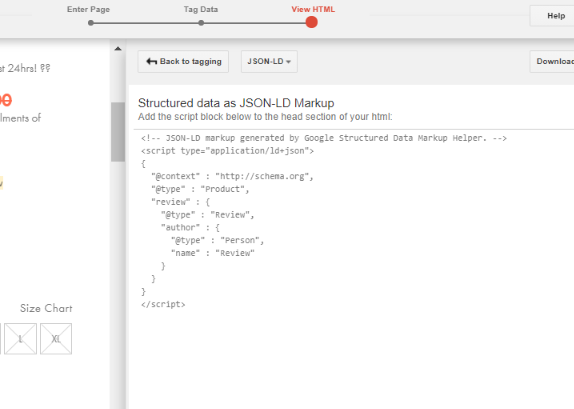
You only need to add this code into the HTML of your page and voila! Now you have added rich snippets to that page.
MOST ECOMMERCE WEBSITES STRUGGLE WITH GENERATING CONSISTENT SALES…WE FIX THAT!
Since 2009, we have helped many ecommerce businesses dramatically increase their online sales. Let us do it for you!
Internal links
When authoritative sites link to one of your pages, that site “sends” some of its domain authority to yours. This is called a “backlink.”
The same happens when you add internal links from one of your most authoritative pages (e.g. your homepage) to another one.
Sadly, most people focus too much on external link building and neglect their internal linking strategy.
To get results, you need to constantly add keyword-rich anchor text links that direct to your top-priority pages.
The navigation of your site is perfect for internal linking, as you’re adding relevant links to your product pages naturally.
But you should also adopt a strategic approach to internal linking and deliberately add links in your product descriptions and other important content areas.
What is technical SEO in ecommerce?
Now that you understand the basics and best practices of on-page optimization, let’s step into technical SEO strategy.
What is technical SEO?
In short, technical SEO involves all the aspects of your site’s architecture and servers, as well as how well search engines can crawl and index your site, including:
- Site speed
- User experience
- Rendering
- Website’s size
- Duplicate content
- Broken links
And some others.
Let’s explore the main ones.
Website architecture
Your site’s architecture dictates how your content and pages are structured and organized.
This is crucial.
If your pages aren’t properly arranged and structured, search engines might not be able to crawl them and index them correctly.
For example, if customers need to click on seven category pages before accessing a specific product page, search engines may struggle to find it.
Worse yet, that page won’t get link equity passed down.

This is especially important for ecommerce sites with a large catalog.
The rule of thumb is that your domain authority should be concentrated into your product and category pages.
Here’s an example of an optimized ecommerce website structure:
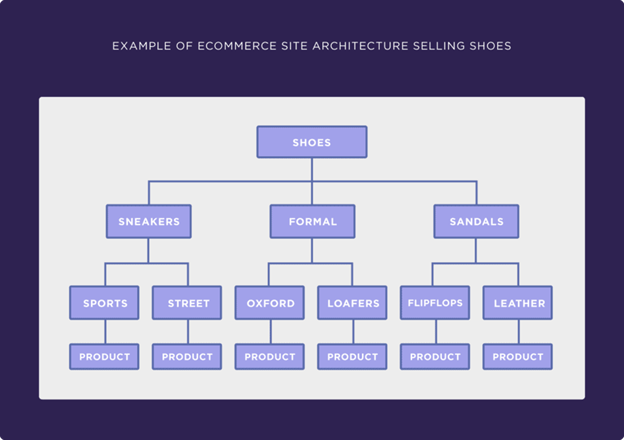
As you can see, it only takes four clicks to reach the homepage.
This type of structure comes with several benefits:
- Better crawling and indexing: A simpler structure will help search engines crawl and index your pages much faster (and more effectively).
- A simplified user experience: Fewer subcategories will help users find specific products in a simple way.
- A more concentrated link authority: Reducing the number of “layers” in your site will help you concentrate link authority on your most important pages.
Number of pages in your site
Number of pages is a huge problem for most ecommerce websites.
Since you’re dealing with dozens, sometimes even hundreds, of products, each requiring a unique page and content, your site can become a complete mess pretty fast.
Dealing with so many pages can create multiple SEO problems:
- Duplicate content
- Broken links
- Abandoned pages
- Increased complexity
The best way to get rid of this problem is by deleting non-performing pages.
If some of your products aren’t selling or people simply don’t find them, there’s no reason why you should keep them.
A quick analysis in Google Analytics can tell you which pages aren’t getting visitors.
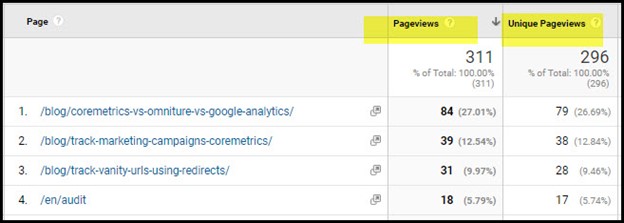
Also, most ecommerce platforms, like Shopify or Bigcommerce, provide you with reports that help you identify products that aren’t selling.
By eliminating these pages, you’ll save yourself from tons of SEO headaches later on.
If for some reason you don’t want to eliminate some pages permanently, you can create a single page containing those products.
Duplicate content
Since the release of Google Panda back in 2011, duplicate content has become one of the major challenges of ecommerce sites.
Most ecommerce sites use a unique URL for each product and product variation (e.g. size, color, type, etc.), which can create duplicate content.
Also, if you have the same product description on multiple pages, Google may see it as duplicate content, and that can hurt your SEO success.
Now, how can you find duplicate content on your site?
Platforms like Raven Tools and SEMRush can help you spot duplicate content pretty quickly.
Simply enter your website URL into the tool and it will show you a detailed report on your most critical SEO issues, including duplicate content.

Once you’ve identified duplicate pages, it’s time to solve the problem.
You can do it in three ways:
- “Noindexing” duplicate pages: Adding a “noindex” tag to a specific page tells Google to “ignore” that page.
- Adding a canonical tag: Canonical tags tell Google that some of your pages are exact copies of a single page.
- Producing original content: This is probably the most difficult solution, but also the most rewarding.
Poor content
There’s a direct correlation between longer content and SEO results.
Research suggests that first page results have 1,447 words, on average.
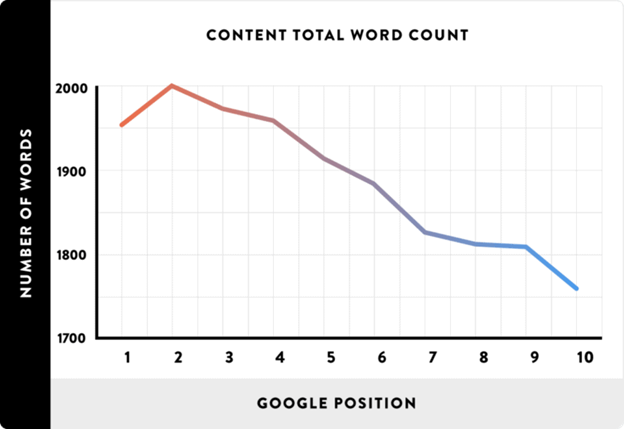
Tha said, the same study reveals that word count alone isn’t enough. Content with higher “Content Grade” on Clearscope, a content optimization platform, seems to rank higher in Google.
According to this study, increasing Content Score by one approximates to boosting rankings by one position.
Clearscope measures things like competition and semantic keywords, which means that longer content isn’t the answer. Comprehensive, relevant content that fully answers a user’s question is.

Here’s the thing:
Producing this type of content is a rough task for most ecommerce businesses.
Most of your content is composed of product descriptions.
If you have 200 products in your catalog, how could you write 200 in-depth pieces of content?
Even though this is challenging, experts suggest that you should add, at least, 500 words worth of content in your product descriptions.
Most ecommerce businesses don’t do it, so this extra work can become a true competitive advantage.
User experience
Improving your site architecture, eliminating non-performing pages, and producing high-quality content is crucial. But if users can’t access that content properly, they’ll have an overall bad experience.
Google doesn’t like that.
Over the next few years, we’ll probably see a dramatic correlation between user experience and search results.
This year, Google has launched a new algorithm update called “Page Experience.”
This update aims to improve user experience by measuring three main signals:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How fast your content loads when users visit your site.
- First Input Delay (FID): How fast users can actually interact with your content.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS: How visually stable your content is when users interact with it.
In other words, your site shouldn’t only load fast, but also provide a smooth experience to users.
Unfortunately, covering these elements in depth is outside the scope of this guide. To learn more about Google’s Core Signals, we suggest you read this guide from Google Search Central.
MOST ECOMMERCE WEBSITES STRUGGLE WITH GENERATING CONSISTENT SALES…WE FIX THAT!
Since 2009, we have helped many ecommerce businesses dramatically increase their online sales. Let us do it for you!
Mobile-friendly ecommerce optimization
Mobile, mobile mobile.
I’m sure you’ve seen the hype of mobile optimization just about everywhere.
But the truth is that it’s not just hype anymore. Mobile is dominating online traffic now.
Last year, roughly 55% of worldwide traffic came from mobile.
It’s rising every year and showing no signs of stopping.
Recently, Google announced that their mobile-first index was rolling out, too.
What does it mean? In a nutshell, the mobile-first index means that Google will be indexing your mobile site first — before your desktop.
This means that your mobile site has to be on-point to continue to thrive on organic SERPs.
If people are landing on your mobile site and bouncing due to bad speeds and horrible UI, you can bet that your rankings will take a hit.
If your website isn’t mobile optimized and responsive, that should be priority number one for your mobile optimization.
On top of that, mobile page speed is critical for success.
What’s the problem with being just a few seconds slower than the “best practice” for speed?
Bounce rates that go through the roof:
If your ecommerce site takes two or more seconds to load, your bounce rate can grow by up to 9%. If it takes five seconds or more, your bounce rate will be around 38%.

Roughly 35% of users’ money is left on the table due to a poor user experience. Meanwhile, improving UX can increase your results exponentially.
User experience and conversion rate optimization in ecommerce are two peas in a pod. With that in mind, you have to make the discovery and buying process as smooth as possible. From UX to cart abandonment rates, optimization is key.
There is possibly no better conversion-optimized website than Rothy’s. Even if you’ve never enjoyed shoes or you aren’t a woman interested in women’s shoes, exploring the site is enjoyable.
When you land on the home page, the site instantly greets you with a simple design that gives you two easy options: menu or shop all.

This is helpful because too many choices can be paralyzing for shoppers.
At the top of Rothy’s home page, a dynamic and changing ticker displays instant value that reassures users that they won’t experience common pain points.
As you scroll down, the options are again consolidated into product styles that are elegant and simple:
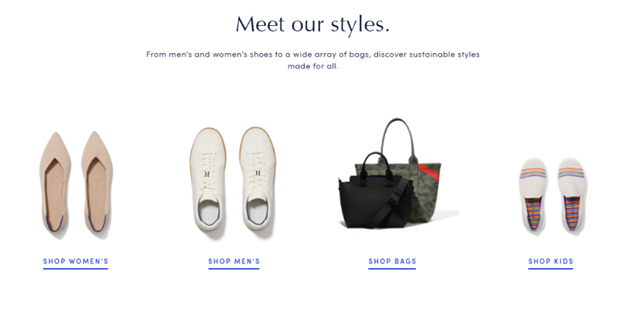
Clicking on individual products opens the product page directly in the window without directing you to another page that might take ten more seconds to load and result in a bounce.
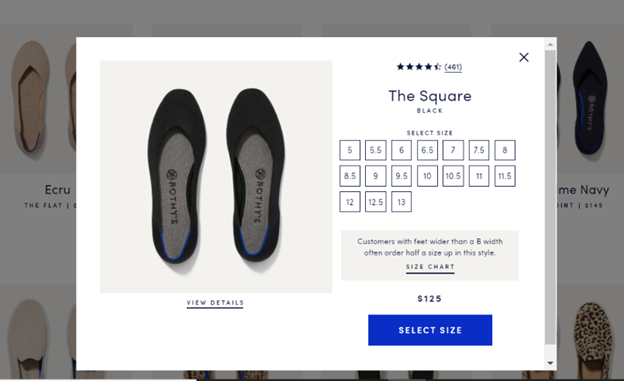
The flow of the site and buying process is virtually unparalleled.
And for the icing on the cake, value is communicated at every single step:
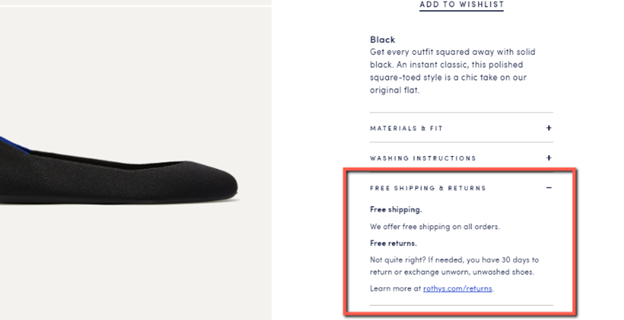
That’s ecommerce conversion optimization.
Here are some best practices that you can follow to ensure that you convert all of your organic traffic:
- Site speed: Make your site faster and prioritize ease of use.
- Navigation: Give fewer, simpler options to find products. Too many choices can cause friction.
- Simplify checkout pages and focus on value: To avoid high cart abandonment rates, always address pain points before consumers have to ask about them.
Amazon in the ecommerce marketplace
You already have an established ecommerce site that’s driving sales.
Why on earth would you turn to Amazon and lose a percentage of your profits?
Back in 2019, Amazon was responsible for 46% of all the ecommerce sales in the United States.
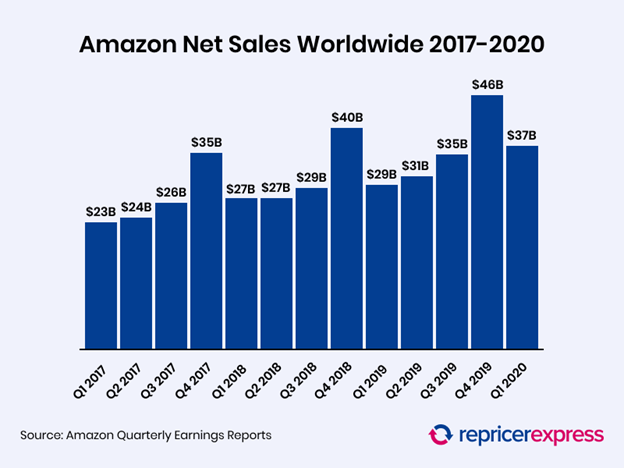
Each month, 214.8 million people visit Amazon, on average.
To put that into perspective, around 332 million live in the U.S. today.
This means that Amazon gets the equivalent in traffic of 64% of the entire U.S population every month.
What does that mean for you?
If you aren’t on Amazon and your competitor is, you can kiss that sale goodbye.
Think about it this way:
Let’s say I’m your typical customer. I want to find a product that your store offers.
So, I start with Amazon. I find the product for a good price, but I still want to browse. I head to Google and find your site. It’s also a good price, but shipping and returns aren’t as clear, and I’ve never purchased on your site before.
Amazon has been loyal to me, and I’ve never heard of your brand.
So I go back to Amazon and buy from your competition for the same price with free shipping and returns.
Yeah, that’s daily life for the majority of online shoppers.
Amazon virtually dominates the ecommerce market.
People love Amazon, and there’s no denying it. The data doesn’t lie.
Plus, brand building isn’t required for selling on Amazon. If someone searches on Google for a product, they’ll naturally choose brands they know over brands they aren’t familiar with.
If they haven’t heard of you, you’ll lose the sale to a competitor.
But on Amazon, anything goes. It’s almost as if your brand is an extension of Amazon. Check out the top reasons why people like to buy from Amazon:
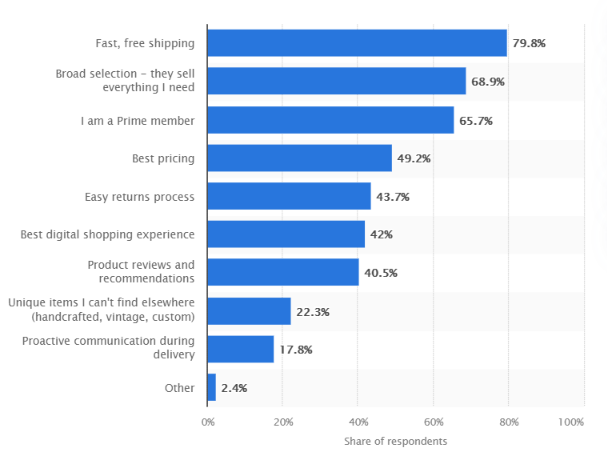
Didn’t see “brand” in there, did you?
If you’re selling on Amazon, the most important factors that go into buying decisions are pricing, reviews, shipping, and Amazon recommendations. Brand recognition is virtually irrelevant.
It’s wise to have both an ecommerce and Amazon storefront. Amazon packs so much traffic and buying power that you can’t ignore it.
If you choose not to have an Amazon presence, you should mimic the benefits of Amazon on products that your competitors are selling on Amazon. Things like free and easy shipping and returns.
If shoppers can’t find similar benefits and they don’t know your brand well, the chances are good that they’ll purchase from your competition on Amazon who likely has good reviews too.
See also: Beginner’s Guide to Amazon SEO
Top ecommerce platforms for SEO
When deciding to host an ecommerce store on the web, you have a bunch of different options, and each packs powerful SEO tools to help you boost rankings.
Here are the top ecommerce website platforms for SEO.
BigCommerce: BC is a top online store platform, and for good reason. It has integrations, SEO capabilities, and the ability to integrate your store on multiple channels like Amazon and Facebook with the click of a button.
Shopify: Like BC, Shopify is a top player for ecommerce. With more advanced SEO options, it’s a great choice for growing stores.
Magento: Magento is another popular ecommerce platform that thrives on Adobe software, which gives you next-level tools and to drive more sales. Magento’s SEO related features also provides a nice advantage over other platforms.
Volusion: Volusion has some of the most picture-perfect and optimized site themes out there. Plus, their digital marketing and SEO tools are great for helping you rank organically.

WooCommerce: WooCommerce directly integrates with WordPress to give you great CMS and online store features.
3dcart: 3dcart allows you to build an online store or simply add a shopping cart feature to an existing website. It also has basic SEO features.
Weebly: Weebly is a popular website building tool with great ecommerce functionality. Weebly integrates with popular shipping carriers and packs tons of SEO tools in the process.
The verdict?
SEO is a huge factor in ecommerce success.
Ranking your website, product pages, and content on the first page of Google will help you secure more organic traffic.
Beyond that, it helps you build brand awareness, which is a big factor in driving sales from organic search results.
Instead of only paying for ads to drive traffic and sales, you can do it organically through powerful SEO.
Turn your efforts to the following key areas of ecommerce SEO that can give you the most bang for your buck:
- Title tags
- Meta description tags
- URLs
- Category / product content optimization
- Mobile optimization
- Schema
- 301 redirects for expired products
- CRO for your ecommerce store
- Amazon
- Picking the right ecommerce platform for your goals
Focus on these best practices, and you’ll drive more organic sales than ever before.
If you feel like you might need professional help to grow your revenue and increase online sales? Check out our ecommerce SEO service and partner with a company with a proven history of success.
MOST ECOMMERCE WEBSITES STRUGGLE WITH GENERATING CONSISTENT SALES…WE FIX THAT!
Since 2009, we have helped many ecommerce businesses dramatically increase their online sales. Let us do it for you!
The post E-Commerce SEO Best Practices for 2021 (Guaranteed to Boost Sales) appeared first on HigherVisibility.
